In this project, I explored a novel approach to classify handwritten digits by combining image and audio data. I expanded the traditional MNIST dataset with spoken audio recordings of the digits, creating a rich dataset that allows for multimodal learning. Using a combination of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Multilayer Perceptrons (MLP) implemented in PyTorch, my model learned to make predictions from both visual and auditory inputs.
Introduction
Handwritten digit recognition is a critical task in various industries such as banking, postal services, healthcare, and document analysis. While significant advancements have been made in the visual recognition of digits, adding audio data can enhance the prediction accuracy by providing additional context. In this project, I combined both images and audio to improve the recognition accuracy.
Method
To achieve this, I processed the MNIST dataset along with corresponding spoken digit recordings. The image data was normalized, and the audio data was prepared for input into the model. I then split the dataset into training and validation sets to ensure robust model evaluation.
Data Preprocessing
The image data underwent min-max normalization to ensure consistency and aid in convergence during model training. The audio data was directly cast to a float32 format suitable for PyTorch.
Model Design
- Image Model: A CNN with 3 convolutional layers followed by 2 fully connected layers, using ReLU activation and max pooling.
- Audio Model: A 3-layer MLP with ReLU activation to handle the audio input.
- Combined Model: Outputs from the image and audio models were concatenated and fed into 2 additional fully connected layers, producing a 10-dimensional vector representing class probabilities.
Model Training
I trained the model for 10 epochs using cross-entropy loss and the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.001. Training was conducted on a GPU to leverage faster computation. The best validation accuracy was tracked to save the optimal model weights.
Hyperparameter Tuning
No extensive hyperparameter tuning was performed, as the initial settings provided satisfactory results.
Results
The combined multimodal model achieved an impressive accuracy of 99.18% on the test set. This highlights the effectiveness of integrating audio data into the digit recognition task. The following figures illustrate the clustering of the image and audio data.
Clustering Visualizations
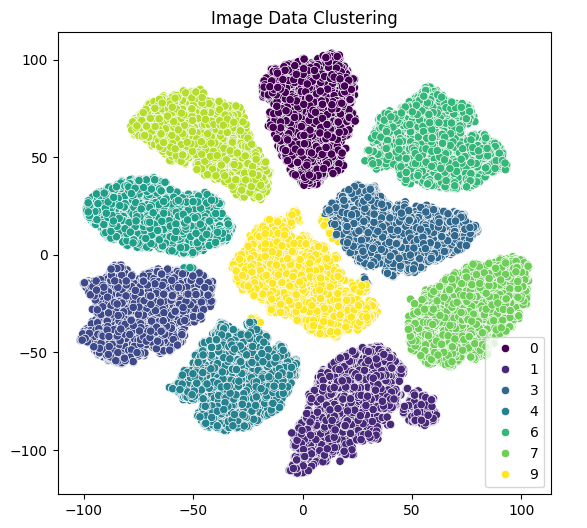
Figure 1: Image data clustering shows distinct clusters for each digit class.
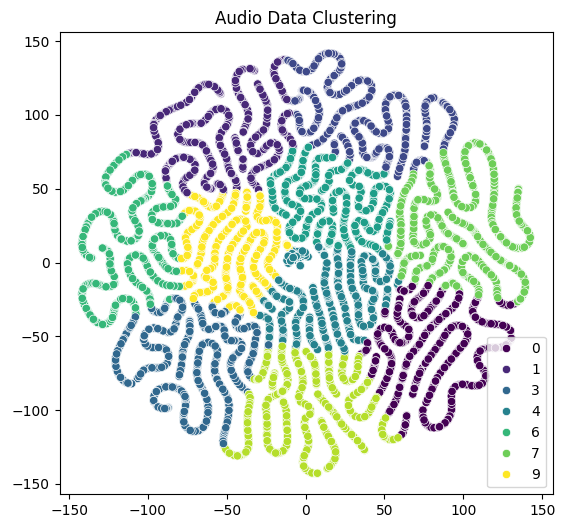
Figure 2: Audio data clustering displays some overlap, indicating challenges in learning distinctive audio features.
Conclusion
My multimodal CNN and MLP model demonstrates the advantages of combining visual and audio data for handwritten digit recognition. Despite achieving high accuracy, the audio model's clustering revealed room for improvement, likely due to variances in audio data such as different accents and noise. Future work could focus on refining the audio processing pipeline to enhance performance further.